Blog:The Best Defense Against Disease: Why You Need Retinal Testing in Houston Before Year-End
Retinal testing is a non-invasive diagnostic method that images the back of the eye to detect early signs of eye disease and systemic conditions. Scheduling your test before year-end can help you maximize insurance benefits and prevent avoidable vision loss. This article explains what retinal testing is, how advanced technologies like ultra-widefield imaging and OCT work, which diseases can be caught early, and why Houston residents should prioritize this essential screening. Many serious conditions, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or early glaucoma, often show no symptoms until damage is advanced. Retinal imaging identifies these changes when interventions are most effective. We'll cover what to expect during an exam, how to utilize vision insurance and FSA/HSA funds, and practical steps for scheduling your local testing.
What Is Retinal Testing and How Does It Protect Your Eye Health?
Retinal testing uses diagnostic imaging to visualize the retina, macula, optic nerve, and blood vessels, detecting structural and vascular abnormalities early. These tests capture detailed photographs or cross-sectional scans, allowing clinicians to spot subtle signs like microaneurysms or nerve fiber thinning long before symptoms appear. Early detection preserves treatment options, enables timely referrals, and often prevents progression to sight-threatening stages. It also offers insights into systemic vascular health, revealing changes linked to hypertension and diabetes.
Retinal testing protects eye health through:
Early Detection: Identifies disease markers before vision loss.
Treatment Planning: Guides timely medical or surgical interventions.
Systemic Clues: Reveals vascular changes prompting evaluation for conditions like hypertension or diabetes.
What Happens During a Retinal Exam in Houston?
A typical retinal exam begins with a brief medical history. Imaging is then performed using devices like ultra-widefield scanners and OCT, a painless, non-contact process. Pupil dilation may be recommended for a full peripheral retina evaluation, which can cause temporary light sensitivity and blurred near-vision. Afterward, the optometrist reviews images, explains findings, and coordinates follow-up. Bring sunglasses and consider a driver if dilation is likely.
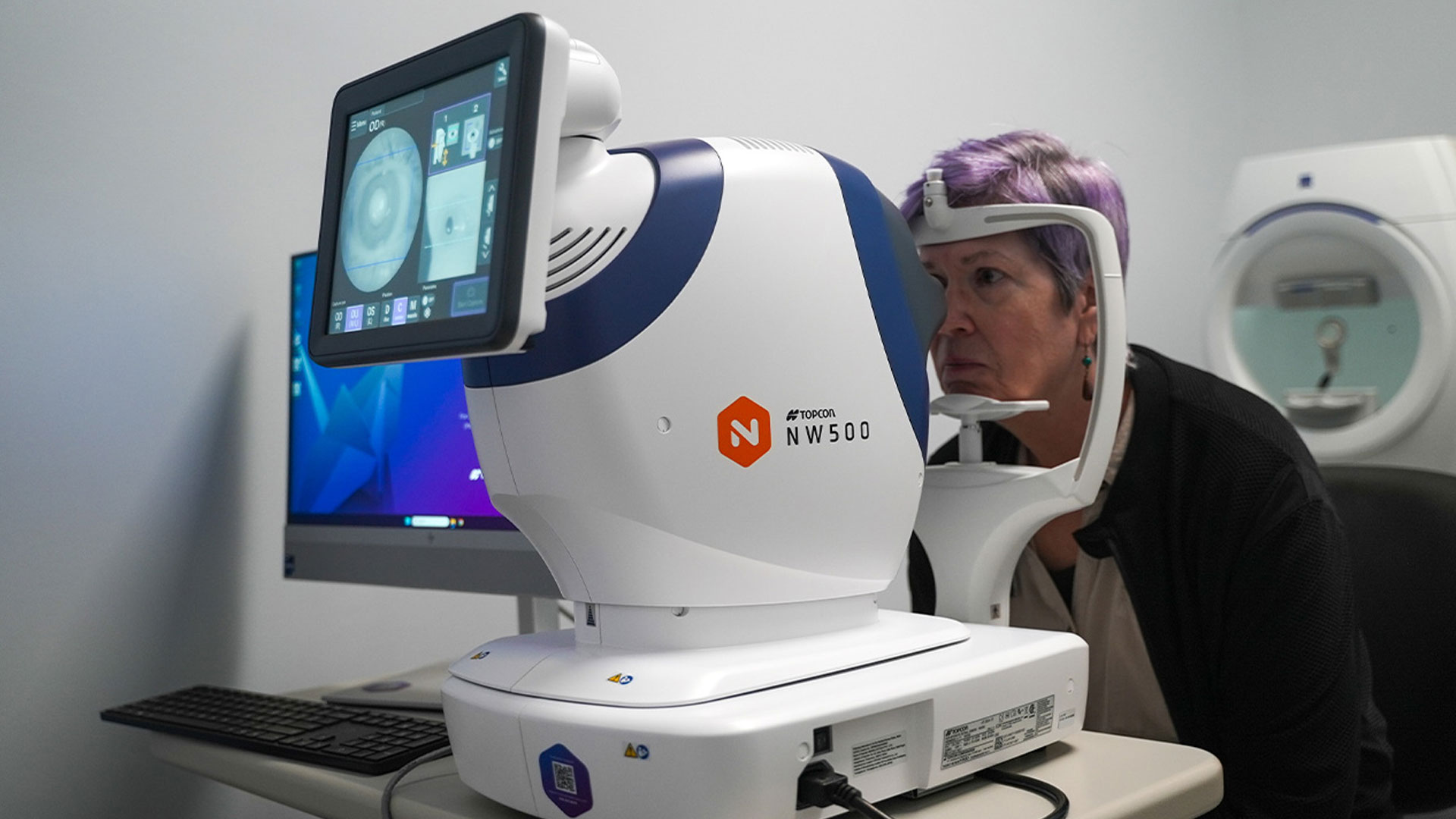
How Does Retinal Imaging Technology Like Optos and OCT Work?
Optos ultra-widefield imaging captures a large portion of the retina in a single shot, revealing peripheral lesions and wider vascular patterns. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) produces high-resolution cross-sectional images of retinal layers, detecting fluid, thinning, or early macular changes. Combining Optos' broad overview with OCT's detailed layer analysis improves diagnostic confidence and enables earlier, more precise interventions. Modern retinal testing often includes both modalities for comprehensive views.
Which Eye Diseases Can Retinal Testing Detect Early?
Retinal testing screens for major ocular diseases by revealing structural and vascular changes before symptoms arise, enabling early intervention. Key conditions detected include diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, and age-related macular degeneration, along with retinal detachment risk factors and systemic vascular signs. Early detection can prompt intensified systemic management or timely ocular therapies. The table below summarizes what retinal testing reveals for key diseases:| Condition | What Retinal Testing Detects | Early Signs and Typical Next Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetic Retinopathy | Microaneurysms, dot-blot hemorrhages, retinal edema | Identify non-proliferative changes; schedule diabetic eye exam intervals and consider laser or injections if edema/proliferation appear |
| Glaucoma | Optic nerve head cupping, RNFL thinning on OCT, visual field defects | Detect structural thinning; initiate intraocular pressure management and regular visual field monitoring |
| Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) | Drusen, pigment changes, subretinal fluid on OCT | Differentiate dry vs wet AMD; monitor progression and refer for anti-VEGF therapy when fluid present |
Diabetic Retinopathy: Why Early Screening is Critical
Diabetic retinopathy, a microvascular complication of diabetes, damages retinal capillaries, leading to vision loss. Early stages are often asymptomatic, making routine dilated retinal screening essential—not just for individuals with diabetes, but also for those who are pre-diabetic or at risk.
Annual exams catch progression early, allowing for timely intervention with laser or injections to preserve sight. Schedule diabetic eye exams in Houston before year-end to utilize benefits and prevent missed opportunities for early treatment.
Glaucoma Detection Before Symptoms Appear
Glaucoma damages the optic nerve slowly, often without early symptoms. OCT quantifies retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness, while visual field testing assesses functional loss. Together, these detect early glaucomatous changes, enabling earlier medical therapy to lower intraocular pressure, slow progression, and preserve central vision. Regular monitoring is crucial for at-risk individuals.
Macular Degeneration Screening for Central Vision
Macular degeneration affects the macula, crucial for detailed central vision. Screening identifies drusen, pigmentary changes, and early fluid accumulation. OCT is sensitive to fluid, a hallmark of wet AMD requiring timely anti-VEGF therapy. Early detection preserves reading and driving ability and enables interventions that stabilize or improve central vision.
Retinal Exams and Systemic Health Issues
Retinal vessels offer a direct view into the body’s microvasculature, revealing changes like arteriolar narrowing or hemorrhages that correlate with hypertensive damage and cardiovascular risk. Detecting these vascular changes often prompts clinicians to recommend systemic evaluation for conditions like hypertension. While not a replacement for blood pressure measurement, retinal imaging provides an objective sign that systemic management may be needed, fostering coordinated care between eye care and primary care providers.
Why Should Houston Residents Schedule Retinal Testing Before Year-End?
Scheduling retinal testing before year-end is crucial for both medical and financial reasons. Many vision or medical benefits, FSA/HSA balances, and insurance authorizations reset or expire with the calendar year. Completing preventive exams now maximizes available coverage. Clinically, avoiding delays reduces the chance of treatable abnormalities progressing, preserving less invasive options and lowering long-term costs. Act now to ensure appointment availability and utilize remaining FSA/HSA funds. The table below outlines common coverage types and recommended actions:
| Coverage Type | Typical Coverage | Action Before Year-End |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Insurance | Medical eye exams and diagnostic retinal imaging when ocular disease or systemic condition is present | Verify benefits, obtain authorizations, schedule a medical eye exam if eligible |
| Vision Plan | Routine eye exams and eyewear allowances | Use routine exam and frame/lens allowances before expiration |
| FSA / HSA | Eligible medical services and diagnostics | Check balances and submit claims for retinal imaging or medical exams before funds expire |
Maximize Your Vision Insurance and FSA/HSA Benefits
Check your FSA/HSA balance and insurer's guidance on diagnostic imaging. Contact your eye care office for appointment availability, claim documentation, and pre-authorization. Schedule covered diagnostic tests and, if applicable, purchase eyewear before deadlines to avoid forfeiture. Retain itemized receipts and submit claims promptly.
- Check Balances: Verify FSA/HSA funds and vision plan limits.
- Confirm Coverage: Ask the insurer if retinal imaging is covered as medical diagnostic testing.
- Schedule Now: Book an appointment and request billing codes.
- Submit Claims: Keep receipts and submit before deadlines.
Risks of Delaying Your Retinal Exam
Delaying screening increases the risk of progressive diseases advancing to stages requiring more invasive or costly interventions. Untreated conditions like diabetic retinopathy or glaucoma can lead to poorer outcomes. Postponement also means losing the opportunity to use expiring insurance or FSA/HSA funds. Proactive scheduling conserves financial resources and ensures timely, effective treatment.
- Worsened Outcomes: Disease may progress beyond less invasive treatment options.
- Higher Costs: Advanced disease often requires more intensive and expensive care.
- Lost Benefits: Expiring insurance or FSA/HSA funds may go unused.
- Functional Impact: Delays can mean avoidable reductions in reading, driving, or work performance.
Why Choose Texas State Optical Briargrove for Retinal Testing in Houston?
Texas State Optical Briargrove offers advanced diagnostic imaging and experienced optometric care for early detection and management of retinal disease. Serving Westheimer, Westside Houston, and the Galleria area, the practice provides comprehensive and medical eye exams, including retinal imaging, glaucoma, and diabetic eye exams. On-site Optos ultra-widefield scanning and OCT enable broad peripheral views and high-resolution layer analysis for improved diagnostic accuracy. Contact the practice directly for scheduling and insurance questions; booking before year-end ensures timely care and benefit utilization.
| Imaging Technology | Scope / Field of View | What It Reveals | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optos (Ultra-widefield) | Large peripheral retina in one capture | Peripheral tears, wide vascular patterns, peripheral hemorrhages | Screening for peripheral pathology and comprehensive retinal overview |
| OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) | Micron-level cross-section of retinal layers | Macular edema, subretinal fluid, RNFL thinning | Detecting macular disease and early glaucomatous structural loss |
| Visual Field Testing | Functional assessment of visual field | Peripheral and central field defects | Correlating functional loss with structural OCT findings for glaucoma |
Meet Dr. Ayesha Butt: Expertise in Eye Care
Dr. Ayesha Butt, the optometrist at Texas State Optical Briargrove, specializes in comprehensive and medical eye care, including diabetic eye exams, retinal disease monitoring, and glaucoma screening. She emphasizes diagnostic evaluation using advanced imaging and patient education, ensuring individuals understand their results and follow-up recommendations. Her approach integrates imaging findings with systemic health discussions and referral coordination when specialist care is needed.
Advanced Retinal Imaging for Early Disease Detection
Combining Optos, OCT, and visual field testing significantly increases sensitivity for detecting both peripheral vascular changes and central structural abnormalities. Optos identifies peripheral lesions, OCT quantifies layer-specific changes, and visual fields link structural loss to functional impact. This multi-modality approach reduces missed diagnoses, guides timely management, and provides objective baselines for longitudinal comparison, leading to better long-term outcomes.
How to Prepare for Your Retinal Exam
Prepare for your retinal exam by bringing a list of current medications and medical history. Arrange transportation if dilation is likely, and allow sufficient time for testing and review. Upon arrival, the clinical team will confirm your history, perform imaging (and any required dilation), and discuss findings. Aftercare typically includes sunglasses for light sensitivity and avoiding driving if near-vision is blurred. Appointment lengths vary from 20-30 minutes for quick imaging to 45-90 minutes for comprehensive exams with dilation and visual fields. Advance planning ensures a smooth experience and maximizes the clinical value of your visit.
Is Pupil Dilation Required and What Are Its Effects?
Pupil dilation may be required for a full peripheral retina examination and clearer images, especially for diabetic retinopathy screening. Dilation temporarily enlarges the pupil, causing light sensitivity and blurred near vision for a few hours. Plan accordingly and bring sunglasses. While some devices allow evaluation without dilation, it remains the gold standard for thorough peripheral assessment. Discuss concerns about driving or activities with the clinic when scheduling.
How Long Does a Retinal Testing Appointment Take?
Appointment length varies: isolated imaging takes 20-30 minutes, while a full medical eye exam with dilation, OCT, and visual fields typically requires 45-90 minutes. Factors like additional testing or extended counseling can lengthen visits. Allow buffer time and bring medical/insurance details to streamline intake. Clinics can advise on expected durations when you schedule.Common Questions About Retinal Testing in Houston
How Often Should I Get a Retinal Exam?
Screening intervals depend on risk. Diabetics typically need yearly dilated retinal exams. Those with glaucoma risk factors may require follow-up every 3–12 months. Low-risk adults often follow an annual or biennial routine eye exam schedule. Discuss your specific risk profile with your eye care provider.
Is Retinal Testing Painless?
Yes, retinal imaging is non-invasive and painless. Cameras and OCT devices capture images without contact. Patients may experience bright flashes of light, and if dilation is used, temporarily blurred near vision and light sensitivity for a few hours. The procedure prioritizes patient safety and comfort.
Does Insurance Cover Retinal Testing?
Coverage depends on billing: medical diagnostic testing for conditions like diabetes or ocular disease is often covered by medical insurance. Routine vision plans cover exams and eyewear. Always check your plan details or ask the clinic to verify benefits and assist with billing codes or pre-authorization. FSA/HSA funds are commonly eligible for retinal imaging and medical exams.
Don't Delay Your Vision Health!
Ensure your eyes are protected and maximize your benefits. Schedule your retinal testing at Texas State Optical Briargrove before year-end.



